Category Archives: Week 8 Assignment
Motors (Week 8)
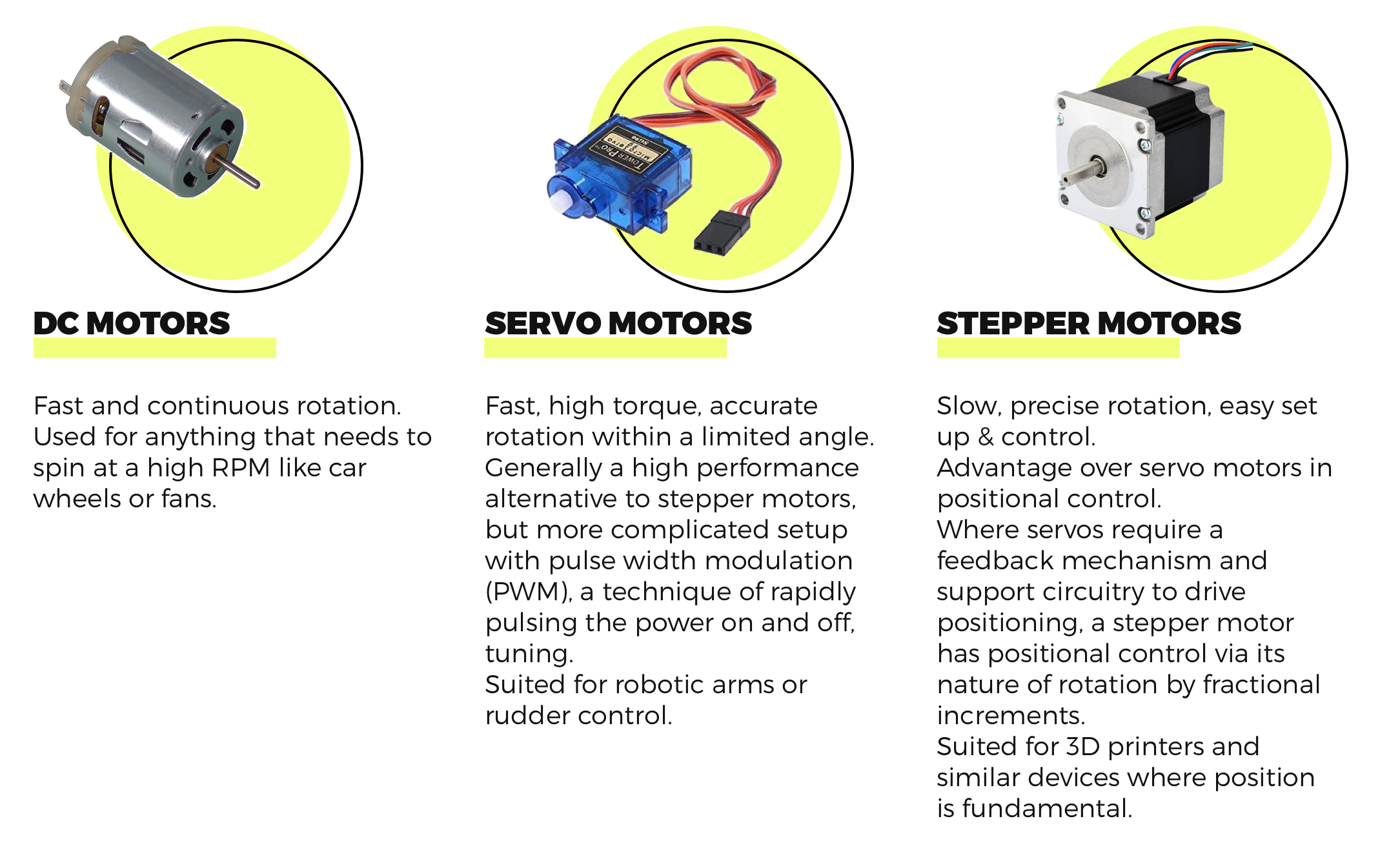
The Difference Between Servo Motors, DC Motors, and Stepper Motors
Servo: A servo motor is capable of precise control of linear or angular motion. This is particularly useful when you want to control the degree of the rotation. Projects that need precision control, such as robotic items, typically use servo motors. Servos determine angles by sending a pulse of electricity for an amount of time. The length of the pulse will determine the angle. A drawback, however, is the range. The rotation is limited to 180 degrees back and forth.
Stepper: A stepper motor uses toothed electromagnets arranged around a central gear. When an electromagnet is powered it attracts the gear’s teeth and aligns them. This process continues for each of the electromagnets creating a rotation. Each of these movements is called ‘steps’ and can make a full 360-degree rotation. A pro feature of this motor is that it doesn’t require power to hold its position. Functionality is quite precise because the steps are built in, however, it sacrifices speed.
DC Motor: DC motors or direct current motors are continuous rotation motors. Unlike a servo motor, where the PWM controls the range of movement, here it controls the speed. The percentage of time spent cycling between on and off determines the speed of the motor. DC motors are fast and have a high RPM, making them good motors for things such as wheels and fans.
Week 8 Assignment
- Write a simple paragraph or any graph to show the difference between DC, Stepper, and Servo Motors.
- Make a circuit using any of the new things you learned today- H bridges/ controlling high current loads OR work with a motor you haven’t worked with before OR Try making a circuit using multiple motors. Document it on the blog per the usual format.